AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Simply Explained
AI/ML in security = misbehave detection. If you ever suffered to get through the forest of buzzwords around the artificial intelligence, then I believe I managed to help you enough with the formula above. However, let's peek under the cover a little bit more.

Short Formula
AI/ML in security = misbehave detection
If you ever suffered getting through the forest of buzzwords around the artificial intelligence, then I believe I've managed to help you enough with the formula above.
However, let's peek under the cover a little bit more.
"It is too dangerous to not discover it now."
AI Can't Get What a Human Can't Get
Let's drop the aura of magic around the things.
If you try to imagine, how to apply AI to some thing, then think about what tasks does the human mind can solve.
It's hard to the human mind to encipher the data with 256-bit cryptographic keys, but it's relatively easy to find implicit dependencies in the context of specific domain.
When a security engineer looks into logs, he is looking for suspicious patterns. It's a job for brain, therefore this job could be accomplished by AI.
Thinking about the practical cases, it's important to think about where the conventional security doesn't help, where the manual efforts of experts are involved: for instance, fighting with the fraud, with the identity theft, with the bots, against the network attacks.
A Few Words About AI Versus ML
AI = ML + NLP + robotics + ...
ML (machine learning) is an ability of machine to learn.
AI (artificial intelligence) is a sort of something bigger than just ML. Still ML is a crucial part of AI.
Basics of Machine Learning
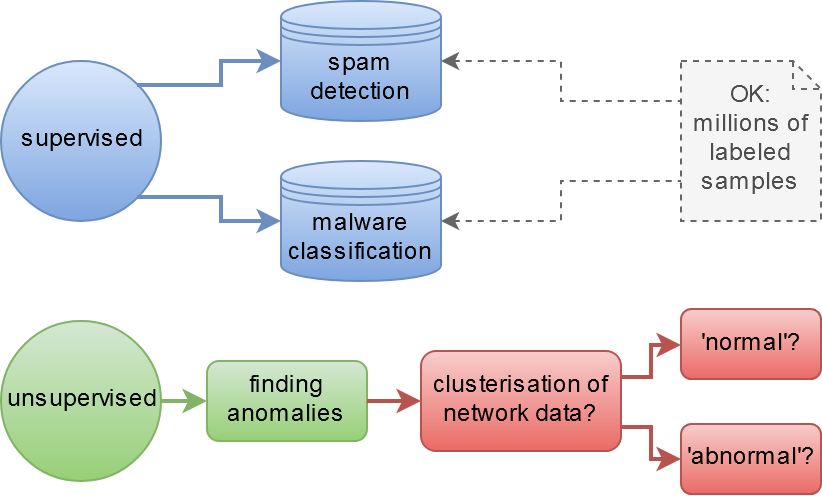
Shortly, there is supervised and unsupervised learning.
-
Supervised learning usually means data classification using a labeled data set. "Labeled" means that a human points either the data is a virus, or spam, or network attack. It works fine in cybersecurity right now: antiviruses, e-mail spam filters.
-
Unsupervised learning deals with grouping of data into some classes (clustering). Final step after clustering is hardly to accomplish: it's need to analyze and to understand what exactly is contained in obtained groups (clusters), and what each group really means.
ML in cybersecurity doesn't mean something mathematically strong like cryptography. The talk is about a probability identifying threats.
"Security is not only about cryptography."
Let's Look at AI/ML Cases in Cybersecurity
Need to notice, that the most of ML/AI solutions are modules of larger complex products, usually it does not represent an entire solution itself.
A lot of startups use a word "AI" and "ML" without publicly available concrete technical details. I haven't put them into my list.
Tip of the day: evade those who tells you "it is good" just because of ML, AI, blockchain, IoT, edge computing, buzz, buzz...
I selected cases of non-classical security applications leveraging AI/ML. The list below represents strictly my personal chart of AI in cybersecurity, and it is not a "TOP 100" of all existing startups which I managed to find on the Internet.
1. Amazon Macie: Detection of Private Data Leakage on the Cloud
📌 Supervised learning
The purpose of cybersecurity is to protect private data. But what is the private data exactly in a heterogeneous environment? AI can be used to classify data finding private data, and security controls can be used to prevent/detect a data leakage. It is not just to analyze logs and data dumps.
What does the Amazon Macie do:
- Monitor data about to identify PII there (PII = Personal Identifiable Data, like payment card number or password).
- Alerting about the probable data leakage, or another threat.
So it is about the data classification, and it is a supervised learning algorithm.
2. AI2 (MIT + PerimeterX): Clustering as a Core of Anomaly Detection
📌 Unsupervised + supervised learning
There is AI2 experiment of MIT and PatternX: after clustering (unsupervised learning) the data is labeled by an expert, eventually turning the task into supervised learning. There are a lot of details in the article.
3. Jask: Network Anomaly Detection
📌 Unsupervised and supervised learning
Jask leverages ML for anomaly detection of network activity. What is good about Jask: they have an own blog with a lot of details about methods they use, particularly about Machine Learning.
4. PerimeterX: Anti Bot Protection
PerimeterX is a SaaS solution where the Machine Learning is used to calculate a score of risk, whether there is a bot, or not.
Unfortunately, I haven't found concrete details about ML applying there. Nevertheless, the case of security is powerful: it is Security as a Service to protect sites against the bots, not a "classic" cybersecurity service.
Learn to Get More
If you are not an expert in ML (machine learning) I would recommend you a Machine Learning Course on Coursera, which I learned, in order to gain a basic awareness in a machine learning field. Really powerful and positive course to be get involved.
Also there are useful articles to overview: